Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sekita, Tsutomu; Tachibana, Haruo; Matsuura, Kenichi; Yamaguchi, Takenori
JAERI-Data/Code 2003-017, 106 Pages, 2003/12
The meteorological observation data at Tokai site were analyzed statistically based on a "Guideline of meteorological statistics for the safety analysis of nuclear power reactor" (Nuclear Safety Commission on January 28,1982; revised on March 29, 2001). This report shows the meteorological analysis of wind direction, wind velocity and atmospheric stability etc. to assess the public dose around the Tokai site caused by the released gaseous radioactivity. The statistical period of meteorological data is every 5 years from 1981 to 1995.
; Ishida, Junichiro; ; Takeishi, Minoru
PNC TN9450 91-006, 30 Pages, 1981/08
Exposure of the public around O-arai Engineering Center (OEC) is estimated in two cases at the ordinary operation and at the postulated accidentsby using the observed meteorological data at OEC. The calculations are done based on the 'Meteorological Guide for Safety Analysis of Nuclear Power Plants' prepared by the Nuclear Safety Commission. According to the guide, the sum of the inverse of wind speed for every direction, atmospheric stability and so on should be used to calculate annual mean concentration of radioactive materials for dose estimation. Health and Safety Division in OEC has been observing wind speed, wind direction, insolation, net radiation and vertical temperature difference. These meteorological data from 1980 t0 1988 are reviewed statistically. The main conclusions of this study are as follows; (1)As the results of examination, the maximun deviation of the observation data at each year is 16 % from the average. The 16 % is within 30 % which is presented in 'Meteorological Guide for Safety Analysis of Nuclear Power Plants'. Therefore it is judged that there is no unusual data between 1980 and 1988. (2)The specific results on the data at 80 meters height are as follows; (a)Average of the most occurance frequencies of wind direction at each year is l8% for the wind from north east. (b)Range of the most occurance frequencies of wind speeds at each year is 5.0 5.9 m/s for the wind from north east. (c)The most occurance atmospheric stability for the wind from north east is D type, whose frequency is about 65%. (3)Average of 'the maximum of annual mean air concentration' around OEC is 4.7
5.9 m/s for the wind from north east. (c)The most occurance atmospheric stability for the wind from north east is D type, whose frequency is about 65%. (3)Average of 'the maximum of annual mean air concentration' around OEC is 4.7 10
10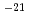 Bq/cm
Bq/cm , and average of 'the maximum effective dose equivalent is 6.9
, and average of 'the maximum effective dose equivalent is 6.9 10
10 Sv/Y, which are based on the caluculations by assuming the release of one Bq per year.
Sv/Y, which are based on the caluculations by assuming the release of one Bq per year.